Designing the perfect flavor blend is both an art and a science, especially in the rapidly evolving world of e-liquids. At the heart of exceptional vaping experiences lies flavor synergy — the intentional combination of aroma compounds to create a sensory experience greater than the sum of its parts.
This synergy isn’t based on guesswork; it’s powered by analytical chemistry, particularly Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS). Flavorists, chemists, and R&D teams use this advanced tool to unlock the molecular secrets behind complementary aromas and engineer blends that are both harmoniously complex and commercially successful.
This in-depth article explores how GC–MS enables vape flavor manufacturers to identify, categorize, and synergize aroma compounds. We will investigate technical workflows, molecular interactions, real-world case studies, and strategic design approaches. All of these converge to form a scientific basis for flavor innovation, with GC–MS providing both qualitative and quantitative insights.
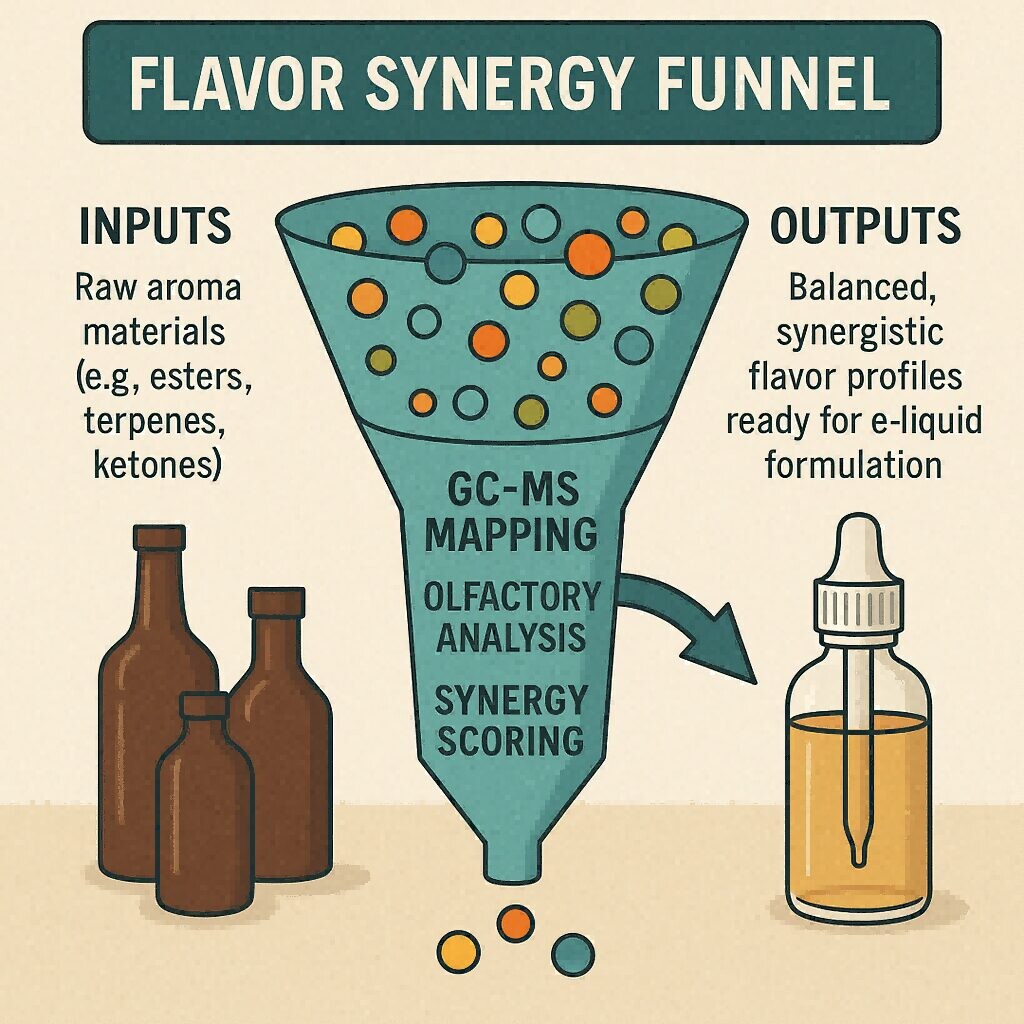
Flavor Synergy Funnel
Flavor synergy occurs when multiple aroma compounds interact to create enhanced or emergent sensory qualities that go beyond individual ingredient perception. For example, combining ethyl maltol (sweet caramel note) with vanillin (classic vanilla) and fruit esters (e.g., ethyl butyrate) can intensify sweetness, improve mouthfeel, and create a longer-lasting aftertaste.
Understanding these interactions requires not just experience, but molecular insight — which is where GC–MS technology excels.
Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) is a compound-specific analysis technique that helps decode complex aroma systems. It separates, identifies, and quantifies volatile compounds in e-liquid formulations or raw concentrates.
(1)Sample Injection: A microvolume of an e-liquid or aroma compound is vaporized.
(2)Chromatographic Separation: The gas chromatograph separates volatile molecules based on retention time.
(3)Mass Detection: The MS component detects and characterizes molecules based on their mass-to-charge ratio.
(4)Spectral Interpretation: Software or manual interpretation identifies compound fingerprints using reference libraries.
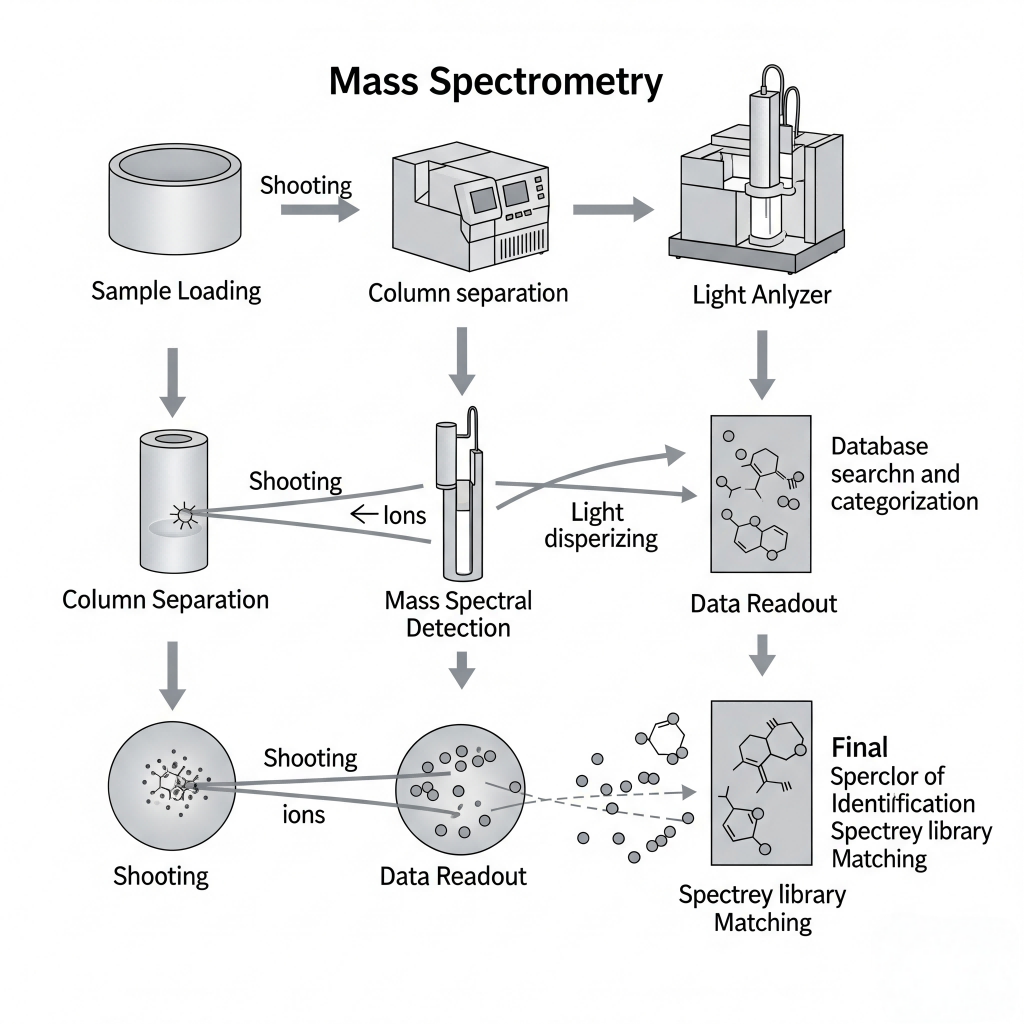
GC–MS Workflow
GC–MS analysis doesn’t just provide a compound list—it enables predictive flavor design. By analyzing volatile compound behavior and comparing known successful profiles, manufacturers can engineer complementary blends with higher success rates.
3.2 Compound Clustering
Aroma Synergy Matrix Chart
Objective: Engineer a novel vape flavor combining tropical mango brightness with herbal complexity, minimizing artificial sweetness.
Step 1: Raw GC–MS Characterization
Step 2: Data-Driven Pairing Strategy
Step 3: Sensory Prototyping
Outcome:
GC–MS identifies what’s there, but the final judge is the consumer. Sensory panels bridge the gap between instrumental data and perceived flavor.
This cycle ensures that scientific hypotheses are validated against human experience — the final goal of any vape flavor.
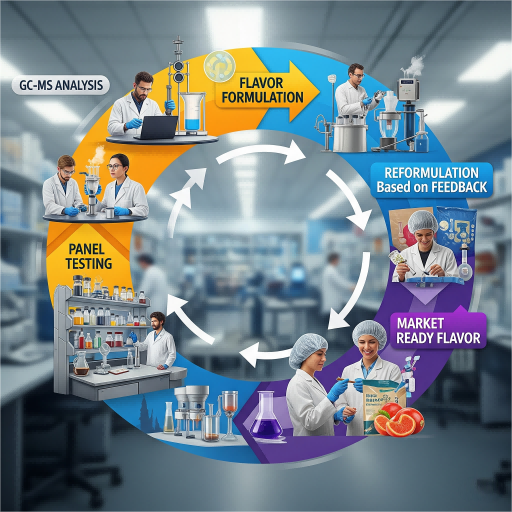
Sensory Feedback Loop Chart
For high-volume manufacturers and white-label brands, GC–MS offers more than development insights — it powers operational efficiency and strategic differentiation.
CUIGUAI Flavoring, a leading Chinese manufacturer of specialized e-liquid aroma concentrates, incorporates GC–MS into all stages of its R&D and production:
Their lab team integrates cutting-edge aroma chemistry with proprietary software to automate blend suggestions based on synergy matrices — resulting in reliable, unique, and scalable flavors.
GC–MS has revolutionized how modern vape flavorists design blends. No longer reliant on trial-and-error alone, R&D teams now harness data to build flavors that are both technically robust and emotionally resonant. When combined with sensory validation, GC–MS empowers a complete, iterative system of flavor development.
As the vape industry matures, market demands for consistency, creativity, and functionality grow stronger. Brands leveraging GC–MS synergy tools — like CUIGUAI Flavoring — are not just keeping up; they are setting the pace.
By aligning chemistry with sensory experience, the future of flavor design looks precise, efficient, and deliciously engineered.
Keywords: GC–MS vape flavor, aroma synergy design, flavor fingerprinting, e-liquid aroma analysis, sensory validation, CUIGUAI Flavoring, vape flavor development, flavor system engineering
Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Jul 10, 2025
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy