Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Dec 03, 2025
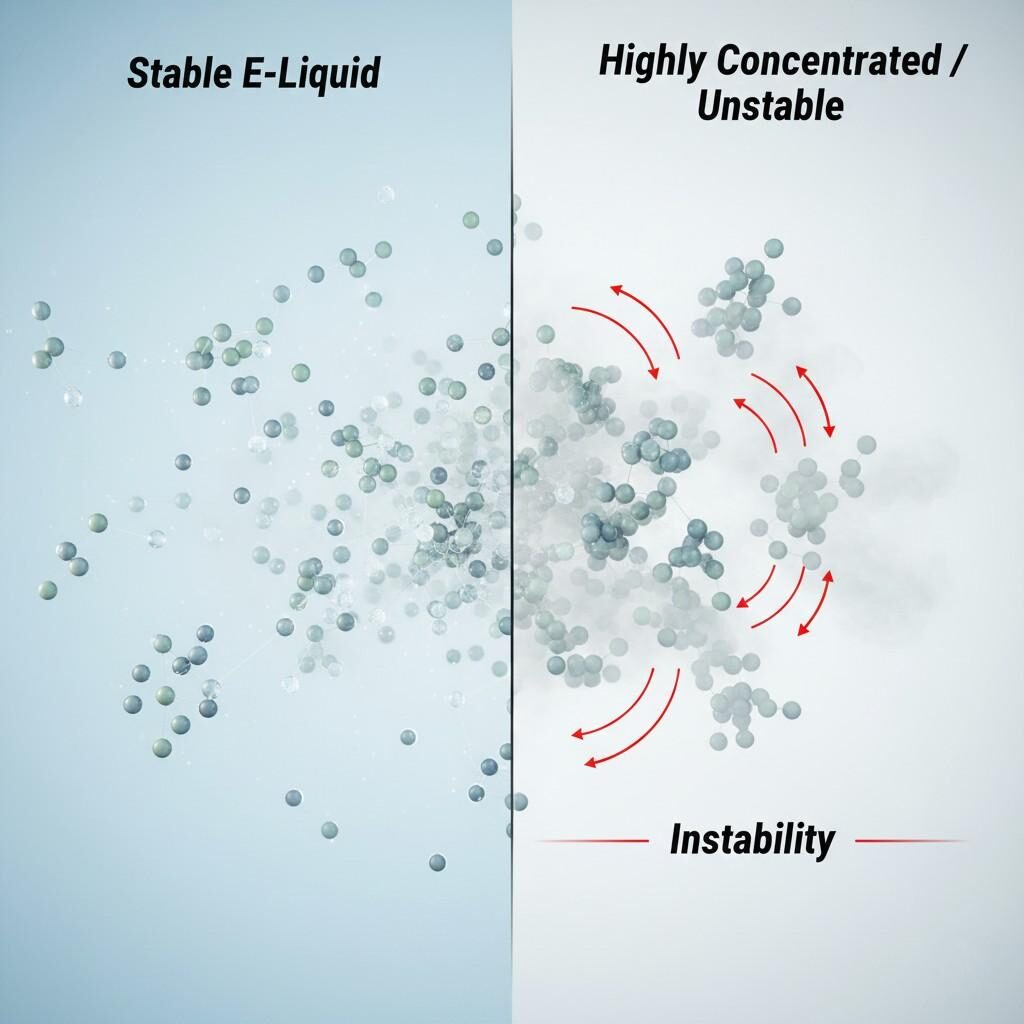
Molecular Order vs. Chaos in E-Liquids
In the modern e-liquid market, the drive for efficiency, portability, and reduced packaging has pushed flavor formulation into a new, complex frontier: Ultra-Concentrates. These concentrated flavor systems—often designed to be diluted at ratios far exceeding the traditional 10-15%, sometimes comprising 50% or more of the final liquid volume—are the backbone of the booming shortfill, longfill, and disposable vape sectors.
For our B2B clients—the manufacturers who depend on these highly potent formulations—the convenience of a concentrate is counterbalanced by a formidable technical challenge: maintaining flavor consistency across the entire product lifecycle.
The perceived simplicity of “just add base” masks a labyrinth of physicochemical interactions. At such high molecular densities, flavor compounds—which are inherently volatile and reactive—do not behave linearly. Their stability, solubility, and sensory profile are constantly threatened by factors invisible to the naked eye.
This technical blog post moves beyond basic mixing guidelines. We will delve into the advanced chemical, physical, and sensory hurdles inherent in formulating ultra-concentrated e-liquids and outline the rigorous scientific protocols required to ensure batch-to-batch and end-user consistency.
The primary challenge of an ultra-concentrate exists before it is ever mixed: its inherent chemical and physical instability. When flavor volatiles are crammed into a minimal carrier solvent (usually Propylene Glycol or a mix of PG/VG), the concentration of individual molecules far exceeds the ideal equilibrium state.
In low-concentration solutions, flavor molecules operate independently. At high concentration, however, the molecules are forced into close proximity. This high molecular density significantly increases the likelihood of unintended molecular interactions (known as aggregation or self-association).
This phenomenon is well-studied in the pharmaceutical industry when formulating high-concentration protein therapies (>150 mg/mL). As detailed in research published in PMC (PubMed Central) focusing on high-concentration formulation development, this crowding exacerbates issues like aggregation, which manifest in our industry as:
Unlike food flavorings, which are often water or oil-based, ultra-concentrates rely on Propylene Glycol (PG) as the primary carrier. PG, though an excellent solvent, is an excipient that must be carefully managed at high concentrations. To maintain stability, specialized stabilizers, co-solvents (like Triacetin), and acid-base buffers are critical. The flavor manufacturer must introduce a buffering system to resist micro-shifts in pH that could trigger the aggregation or chemical degradation of pH-sensitive flavor components (e.g., some esters or citrus notes).
High concentration accelerates the degradation pathways caused by external factors:
The most frustrating consistency challenge for clients is the behavior of the flavor profile after dilution. The assumption is that if a flavor is mixed at 10%, it will taste precisely half as strong as one mixed at 20%. This is the Dilution Paradox—flavor profile changes are fundamentally non-linear.
Human olfactory receptors have different detection and saturation thresholds for every chemical compound. In an ultra-concentrate, the sheer concentration of all compounds (desired flavors, solvents, and trace impurities) creates a saturated, sometimes harsh sensory experience.
When diluted:
For large-scale manufacturing consistency, the method of dilution matters greatly.
Research from the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association (FEMA) underscores the need for consistency, particularly in large-scale mixing, where slight deviations in concentration or technique can lead to thousands of off-spec units. This is why a concentrate’s CoA must include highly specific volumetric-to-gravimetric conversion factors.
Ultra-concentrates often require longer steeping times than standard e-liquids because their molecular starting point is so far from equilibrium. Consistency is challenged by the maturation process itself:
A professional concentrate must be engineered for a predictable and accelerated steeping curve, ensuring that the profile at Day 7 closely resembles the profile at Day 30, thereby eliminating a major variable for the client.
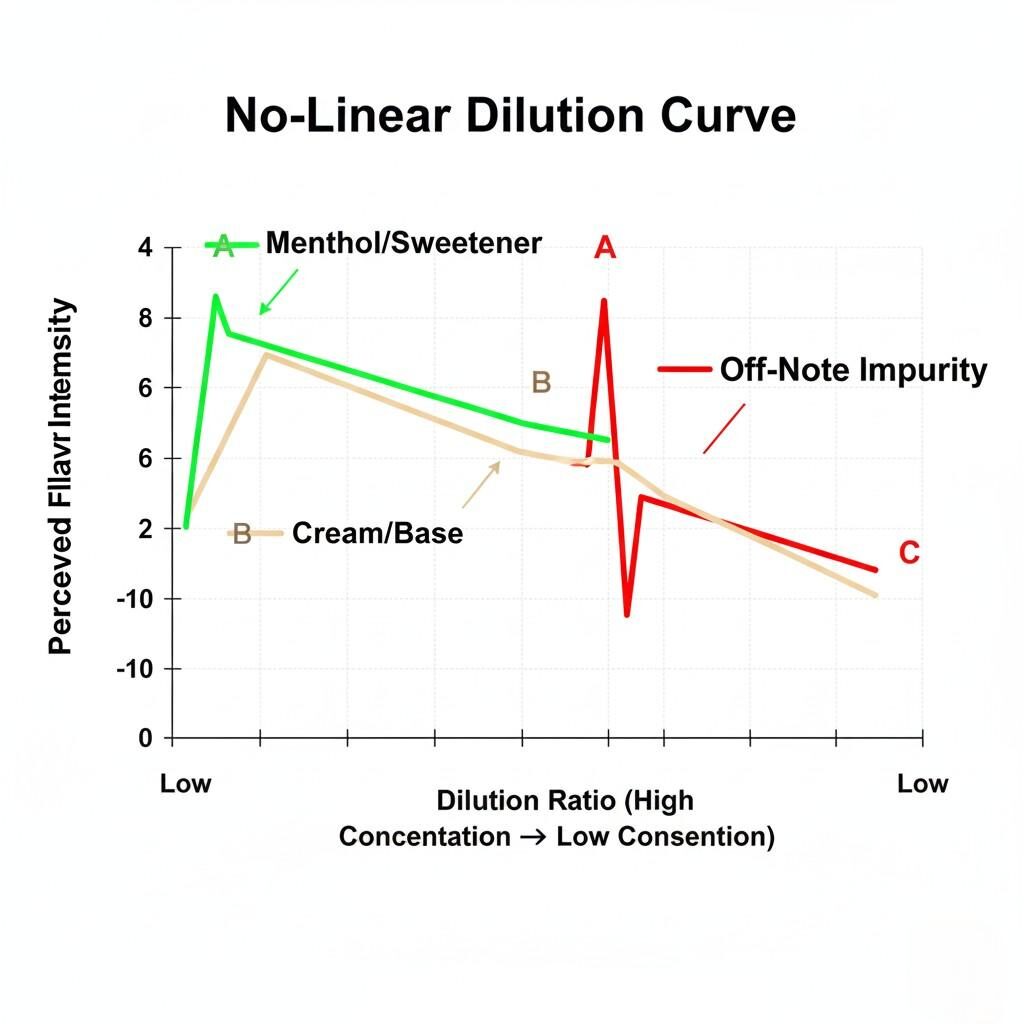
Non-Linear Dilution Curve
Once the ultra-concentrated flavor is successfully diluted and packaged, its consistency is still at the mercy of the end user’s device. For the flavor manufacturer, this requires formulating for a worst-case scenario.
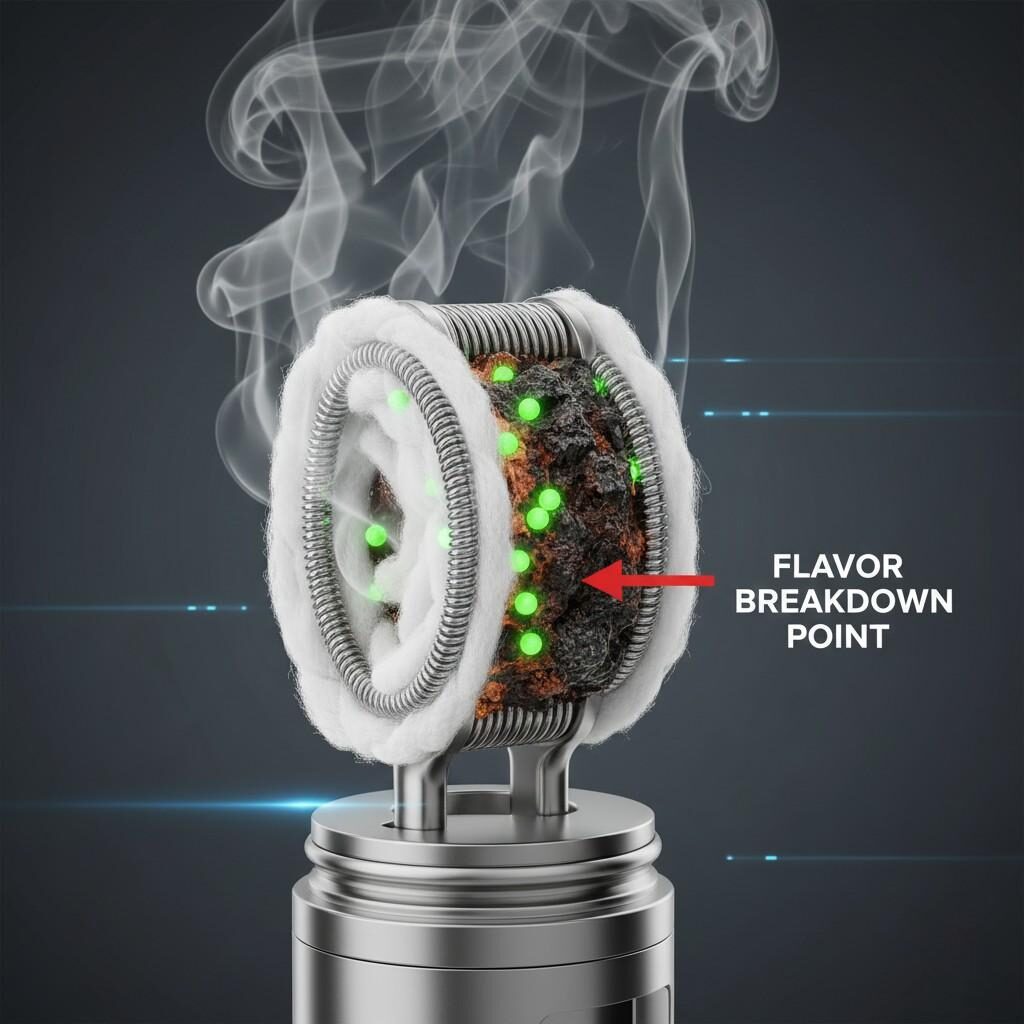
Modern sub-ohm and high-power disposable devices operate at high wattage, subjecting e-liquid to intense thermal stress. This stress can break down flavor molecules through pyrolysis, creating aldehydes and other potentially harmful compounds.
Crucially, some flavorants actively promote chemical instability under heat. Research published in PMC (PubMed Central) in Toxicology Letters demonstrated that flavorants like dipentene, citral, and linalool promoted free radical formation in a concentration-dependent manner within e-cigarette aerosols (Source 4.5). This has two major consistency implications:
The solution is to use thermally stable flavor chemicals and antioxidant-like excipients (such as certain forms of Vitamin E or specific flavor esters like Ethyl Vanillin, which was shown to inhibit radical formation) to fortify the concentrate against high-wattage use.
Ultra-concentrates, especially those formulated for disposable vapes, often contain highly concentrated sweeteners (Sucralose) and cooling agents (WS-23). The consistency of the final flavor is ruined when these additives deposit rapidly onto the heating coil—a phenomenon known as coil gunking.
The manufacturer’s challenge is to find the minimum effective concentration of these agents to provide the desired sensory impact without causing rapid flavor degradation through hardware failure. This requires formulating with higher-purity, lower-residue versions of these additives and optimizing the flavor profile to rely on non-degrading flavor esters for sweetness and mouthfeel, reducing the dependence on physical sweeteners.
The final consistency is defined by perception, which is drastically altered by the device’s airflow.
The most consistent ultra-concentrates are engineered with multiple flavor layers, allowing different notes to remain detectable across various power settings and airflow restrictions.

Sub-Ohm Coil Flavor Breakdown
For our manufacturing clients, we advocate for a structured, science-driven system that mitigates the aforementioned risks. This system relies on analytical validation far surpassing standard quality control.
Before any ultra-concentrate leaves our lab, it must be chemically fingerprinted. We utilize Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) to separate and quantify every single volatile organic compound.
To guarantee a 24-month shelf life, we employ rigorous accelerated stability testing, in line with protocols often adapted from FDA guidelines for stability testing of drug products.
The final arbiter of consistency is the human palate.
The age of ultra-concentrated e-liquids demands an equal elevation in formulation science. The challenges of high-density aggregation, non-linear dilution profiles, and thermal stability in the face of diverse hardware are too significant to overcome with conventional mixing methods.
For manufacturers focused on large-scale production, global compliance, and premium quality, consistency is not a luxury—it is a mandatory asset. By integrating advanced analytical chemistry, rigorous stability testing, and human sensory validation, we transform the inherent instability of ultra-concentration into the hallmark of a reliable, high-performance product.
Partner with us to master the molecular crucible and deliver flavor consistency that builds brand loyalty, batch after batch.

E-Liquid QA & Sealing
Is your current flavor supplier struggling with batch-to-batch consistency in your concentrated product line?
We specialize in Ultra-Concentrate Stabilization and Transfer Efficiency. We offer a Complimentary Technical Consistency Audit of your current formulation or a Free Sample Batch engineered to meet your exact stability and sensory requirements.
📧 Email: [info@cuiguai.com]
🌐 Website: [www.cuiguai.com]
📱 WhatsApp: [+86 189 2926 7983]
☎ Phone: [+86 0769 8838 0789]
Contact us today to ensure your next batch is as consistent as your first!
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy