Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Nov 15, 2025

Modern Aroma Lab & Formulation
In the competitive world of electronic liquid (e-liquid) flavor manufacturing, success depends on how fast a company can create and validate new flavors—without compromising stability, safety, or sensory quality. Consumers demand novelty: tropical fruit explosions, creamy dessert bases, and authentic tobacco blends. Yet, every innovation must also meet the highest standards of chemical consistency, thermal stability, and regulatory compliance.
For a manufacturer, developing 100 stable flavors is not just an achievement—it’s an engineering system that blends chemistry, sensory science, and quality management. The process involves data-driven formulation, raw material traceability, accelerated stability testing, and structured creativity.
This article provides a technical roadmap for how leading flavor manufacturers like CUIGUAI Flavoring can efficiently develop and stabilize 100+ e-liquid flavors while maintaining precision, reproducibility, and compliance across global markets.
Flavor stability refers to the ability of a flavor formulation to maintain its sensory and chemical integrity under normal storage, transportation, and usage conditions. In scientific terms, it involves controlling:
A stable flavor maintains its profile, strength, and clarity over its intended shelf life, typically 12–24 months.
For consumers, stability equals trust. An unstable flavor may darken, lose aroma intensity, or even develop unwanted notes after just weeks of storage. This can lead to:
According to the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association (FEMA), stability and safety are foundational to ensuring consumer confidence in flavor products (FEMA, 2023).
To develop 100 stable flavors quickly, a manufacturer must balance speed and science. Modern flavor houses use data-driven formulation pipelines—where analytical chemistry, sensory evaluation, and AI-based prediction models guide rapid iteration.
Let’s explore the pillars of this approach.
A successful flavor program starts with an ingredient intelligence database. This database catalogs:
Such databases allow formulators to predict interactions and design stable blends faster. Many manufacturers integrate this data with GC–MS reference chromatograms and internal sensory panels.
Rather than starting each flavor from scratch, leading companies use a modular design approach:
This modular system enables the creation of 100+ distinct flavors through structured recombination, reducing development time by over 60%.
According to a 2022 study in the Journal of Food Science, modular aroma design and pre-characterized ingredient databases significantly improve flavor reproducibility and shorten R&D timelines (Journal of Food Science, 2022).
Every new flavor is analyzed using Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) to ensure purity and detect potential reactive compounds. This analytical fingerprint helps predict:
The combination of GC–MS + sensory evaluation forms the backbone of rapid yet controlled innovation.
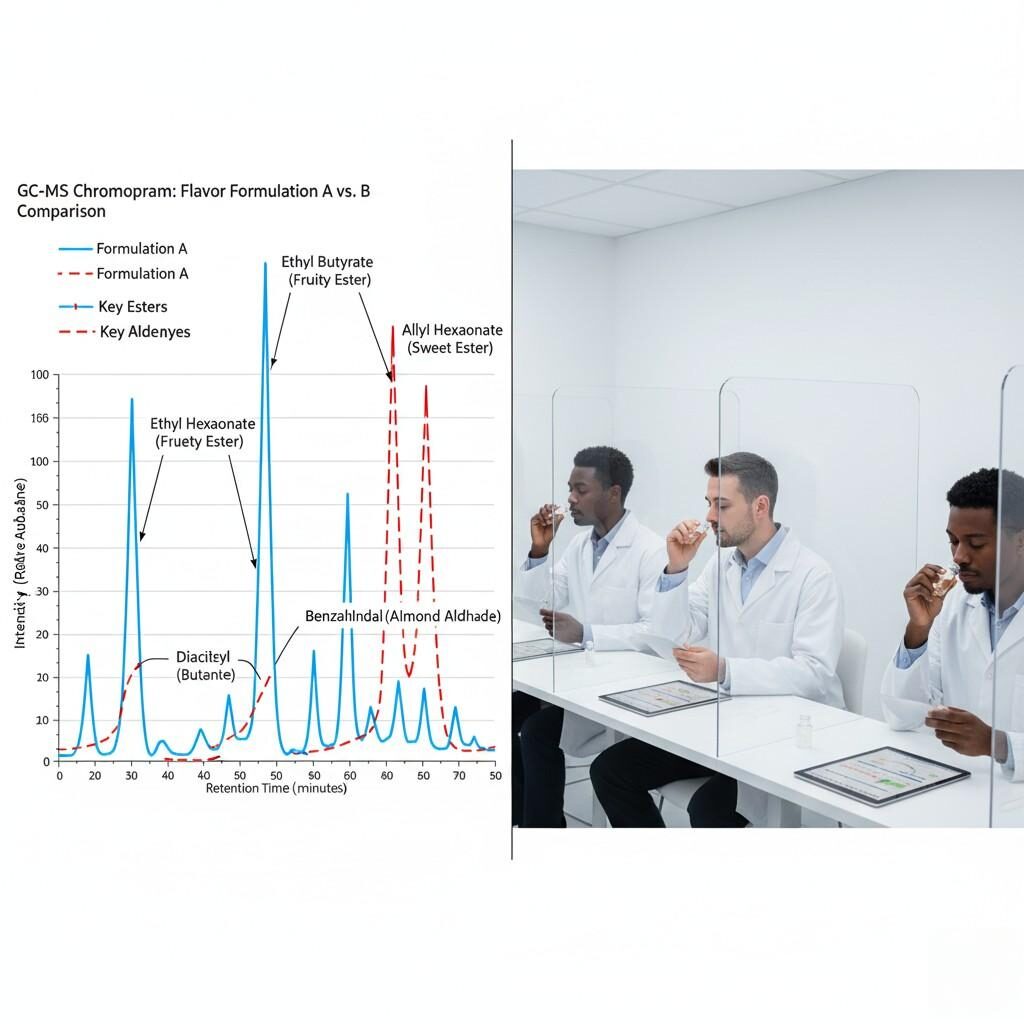
E-Liquid Flavor GC-MS & Sensory
Oxidation is the primary cause of flavor degradation. Compounds like vanillin, benzaldehyde, or limonene oxidize easily, producing off-notes or color shifts.
To control oxidation:
The U.S. National Library of Medicine notes that oxygen exposure accelerates the breakdown of volatile organic molecules in food and fragrance systems, especially under light and heat (PubChem, 2024).
The carrier system—usually propylene glycol (PG) and vegetable glycerin (VG)—influences solubility and volatility.
Solvent polarity and viscosity directly affect molecular dispersion, flavor strength, and storage stability.
Some flavor molecules (like vanillin or citral) are sensitive to pH shifts and react with nicotine bases or acids. To prevent unwanted reactions:
High-speed blending without temperature or oxygen control can damage fragile compounds. Modern flavor factories use:
CUIGUAI Flavoring employs such controlled systems to preserve volatile esters and maintain aroma precision.
To certify a flavor as “stable,” it must undergo accelerated stability testing—simulating months of storage in just weeks. Tests typically involve:
Data is recorded using chromatographic peak area analysis and organoleptic scoring.
| Parameter | Method | Purpose |
| Peroxide Value | Titration | Detects oxidation progress |
| GC–MS fingerprint | Analytical chemistry | Monitors compound stability |
| pH drift | Electrometric | Identifies acid/base instability |
| Sensory evaluation | Panel testing | Tracks aroma consistency |
These results are compiled into a Stability Index, used to classify flavors into categories:
Machine learning models trained on historical stability data can predict which new formulations will likely remain stable.
Using such predictive analytics can reduce real-world testing time by up to 50%, accelerating flavor development from months to weeks.
According to MIT’s Chemical Engineering Department, predictive modeling and machine learning are transforming formulation science across food, cosmetic, and vaping industries by enabling faster, data-backed innovation (MIT OpenCourseWare, 2023).
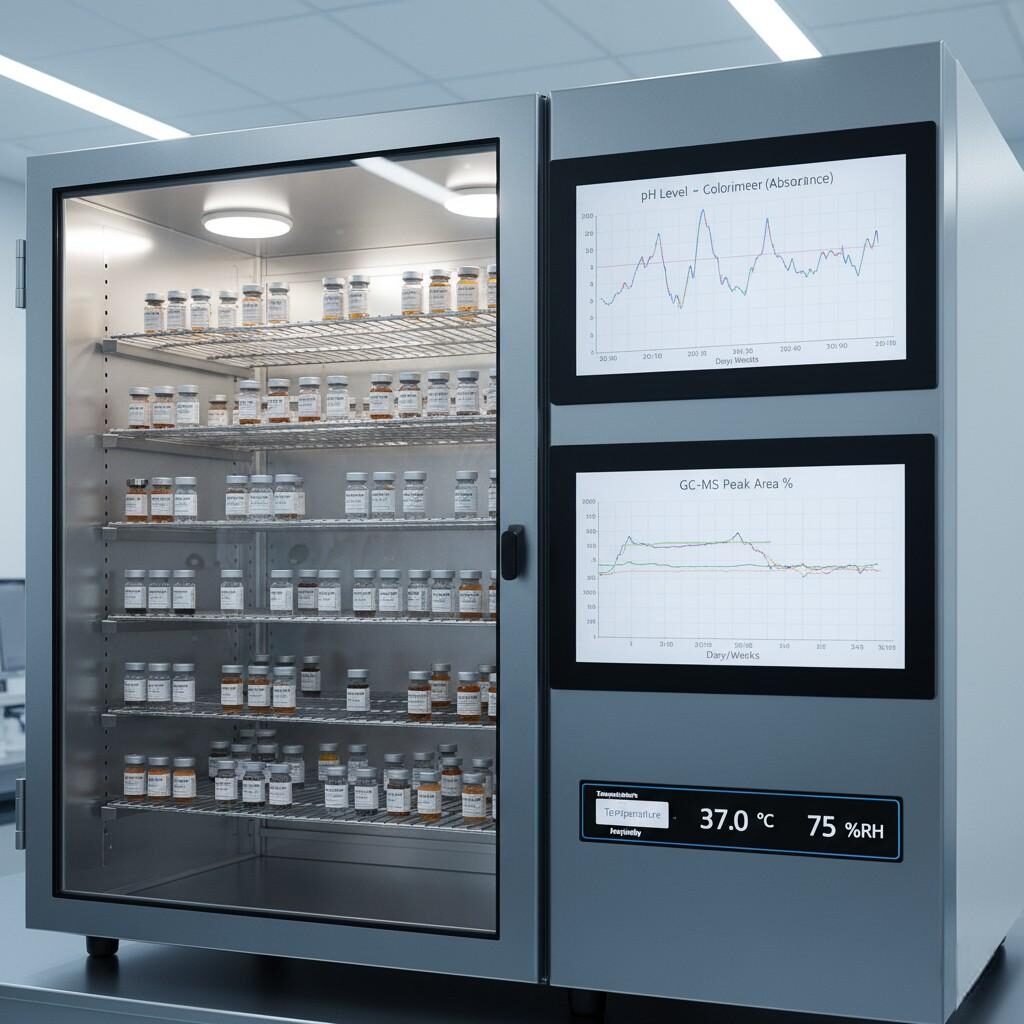

E-Liquid Stability Testing
To create 100 stable flavors efficiently, companies need an organized workflow combining chemistry, sensory, and production engineering.
A digital Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) system ensures traceability across all stages.
Dividing R&D teams into thematic clusters (e.g., Fruit, Dessert, Beverage, Tobacco, Mint) allows parallel progress. Each team maintains its own mini flavor library, contributing to the 100-flavor target collaboratively.
Each stable flavor must be accompanied by:
Having these ready shortens the PMTA/TPD submission process later.
Impure ingredients introduce instability. Collaborate only with suppliers offering:
CUIGUAI Flavoring employs a three-tier supplier audit system:
This ensures raw material uniformity, preventing variability across hundreds of flavor formulations.
Scaling up a stable prototype to full production requires careful process control.
Each flavor batch must follow identical:
Automated PLC systems ensure reproducibility, minimizing human error.
Containers must prevent oxygen, UV, and moisture ingress. Amber glass or coated PET bottles are standard for sensitive flavors.
CUIGUAI Flavoring also uses inert gas filling and vacuum sealing for long-term stability during export.
With 100+ flavors, data management becomes a core challenge.
A centralized digital platform can manage:
Such systems simplify regulatory reporting and client communication, especially for PMTA or EU-TPD submissions.
Even the most advanced analytical data must align with human sensory evaluation. CUIGUAI Flavoring integrates:
Consistency between instrumental data and human perception defines final product success.
Fast development often risks instability, but modern science allows both speed and stability.
The key is building predictive control at every step—from ingredient selection to final shelf testing.
At CUIGUAI Flavoring, we see the creation of 100 stable flavors not as mass production but as 100 parallel scientific achievements, each rooted in chemistry, technology, and sensory design.

Flavor Development & Evaluation Collage
The ability to develop 100 stable flavors rapidly is not luck—it is the result of scientific discipline, data intelligence, and manufacturing excellence.
By integrating chemical analytics, predictive modeling, GMP production, and sensory expertise, a manufacturer can innovate faster while ensuring every flavor meets global safety and quality expectations.
CUIGUAI Flavoring stands at the intersection of creativity and compliance, offering:
For technical collaboration, PMTA documentation support, or free sample requests, contact our technical team today:
📧 Email: [info@cuiguai.com]
🌐 Website: [www.cuiguai.com]
📱 WhatsApp: [+86 189 2926 7983]
☎ Phone: [+86 0769 8838 0789]
Let’s build the next generation of stable, compliant, and innovative flavors together.
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy