Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Sep 26, 2025

China Vape Regulation – Labeling Requirements
The vape industry in China has grown into the world’s most influential production hub, supplying over 90% of global vaping hardware and a substantial share of e-liquid formulations. With this dominance has come intense regulatory oversight. Since 2021, the State Tobacco Monopoly Administration (STMA) has progressively introduced detailed rules that govern e-cigarettes, e-liquids, and their ingredients, including aroma blends used as flavoring concentrates.
For companies producing aroma blends, labeling is no longer a simple matter of putting a name on a drum. It is a technical, legally binding, and strategically critical task. Labels now serve as compliance documents, supply chain communication tools, and brand credibility indicators. Missteps—whether omissions, vague descriptors, or incorrect chemical identifiers—can result in costly delays, penalties, or even market exclusion.
This article, exceeding 2500 words, is designed as a comprehensive technical and strategic guide for vape flavor manufacturers, e-liquid producers, and regulatory professionals. It outlines the current Chinese labeling requirements for aroma blends, explains the analytical science behind accurate labeling, and presents strategic approaches to compliance and competitive positioning.
China’s vape regulation has moved from ambiguity to specificity. Once managed at a provincial level with minimal enforcement, today’s vape industry falls under centralized STMA oversight.
Key regulatory drivers include:
Labeling obligations directly affect aroma suppliers because ingredient transparency is mandated. Manufacturers must not only declare finished e-liquid compositions but also ensure upstream suppliers provide reliable, compliant labeling for their concentrates.
According to the STMA’s official release:
“Electronic cigarette products must truthfully reflect ingredient composition and maintain full traceability in supply chain documentation.”
(Source: Government of China, STMA official regulation portal)
This creates dual responsibilities:
Unlike single molecules such as nicotine or menthol, aroma blends are complex chemical matrices. A single “tropical fruit” flavor might contain over 30 molecules from diverse classes.
Common classes of vape aroma molecules include:
Each category poses different analytical and regulatory challenges. Aldehydes, for example, require strict concentration control due to toxicity concerns, while esters may degrade during storage, complicating traceability.
Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) is the cornerstone of flavor analysis. Yet, GC–MS alone cannot always differentiate isomers (e.g., linalool vs geraniol). Complementary methods such as LC–MS, FTIR, and GC–Olfactometry are often needed for robust identification.
This means that accurate labeling requires technical infrastructure, not just marketing expertise.
Wikipedia notes on food additives reflect how regulatory agencies worldwide differ in permitted lists, creating cross-border inconsistencies (Source: Wikipedia, Food additive). China follows its own pathway, with STMA-approved positive lists serving as the gold standard.
A marketing name like “Juicy Mango Ice” may attract consumers, but regulatory labels must instead declare:
Precision is mandatory: vague “flavor blend” descriptors are not accepted in regulatory filings.
Labeling is more than compliance—it is a strategic differentiator.
This approach balances regulatory transparency and IP protection.
QR codes and blockchain-enabled records allow regulators and clients to instantly verify ingredient authenticity. By embedding traceable digital labels, aroma suppliers reduce disputes and speed up regulatory approvals.
A 2023 report by China Insights Consultancy emphasized digital traceability as a major compliance trend (Source: CIC Research Report on China’s E-cigarette Industry, 2023).
For suppliers aiming at both domestic and export markets, harmonized labels are essential. Aligning with:
prevents costly re-labeling and establishes global credibility.
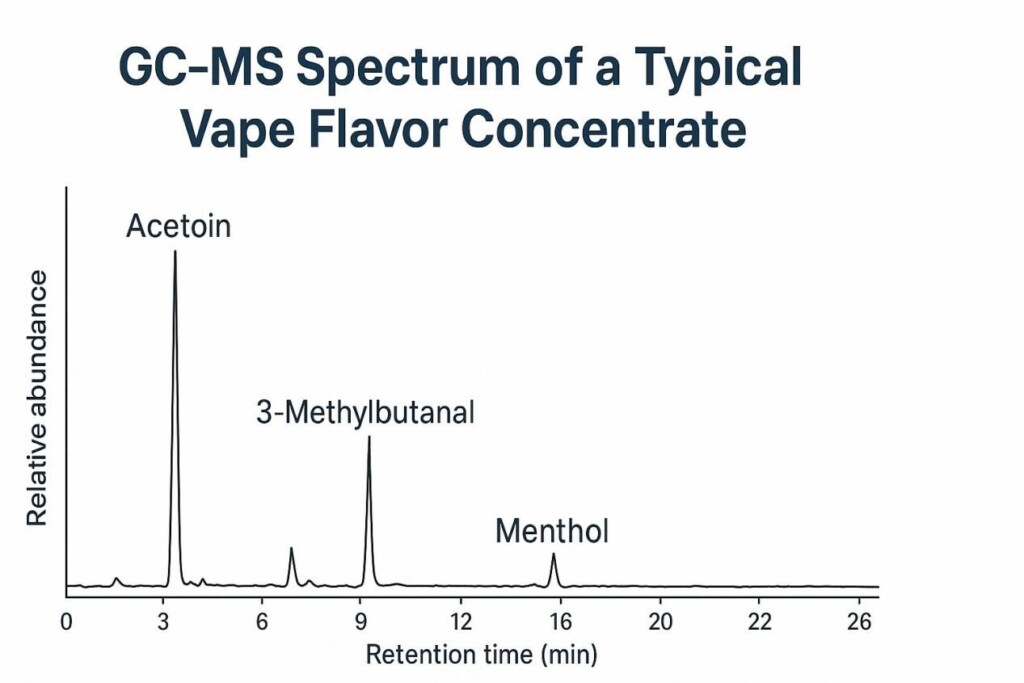
GC–MS Spectrum of Vape Flavor Concentrate
To help aroma blend manufacturers build robust systems, a step-by-step framework is recommended:
A compliant China aroma blend label must include:
A supplier used exact CAS identifiers and disclosed ethyl butyrate, isoamyl acetate, and delta-decalactone concentrations. Approval was granted within 6 weeks, saving downstream clients time.
Another supplier listed “WS-23 derivative” without CAS numbers. This vague disclosure triggered regulatory rejection, delaying exports by 3 months.
A manufacturer embedded encrypted QR codes into drum labels. Regulators accessed formula data instantly, reducing inspection times by 50% and earning client trust.
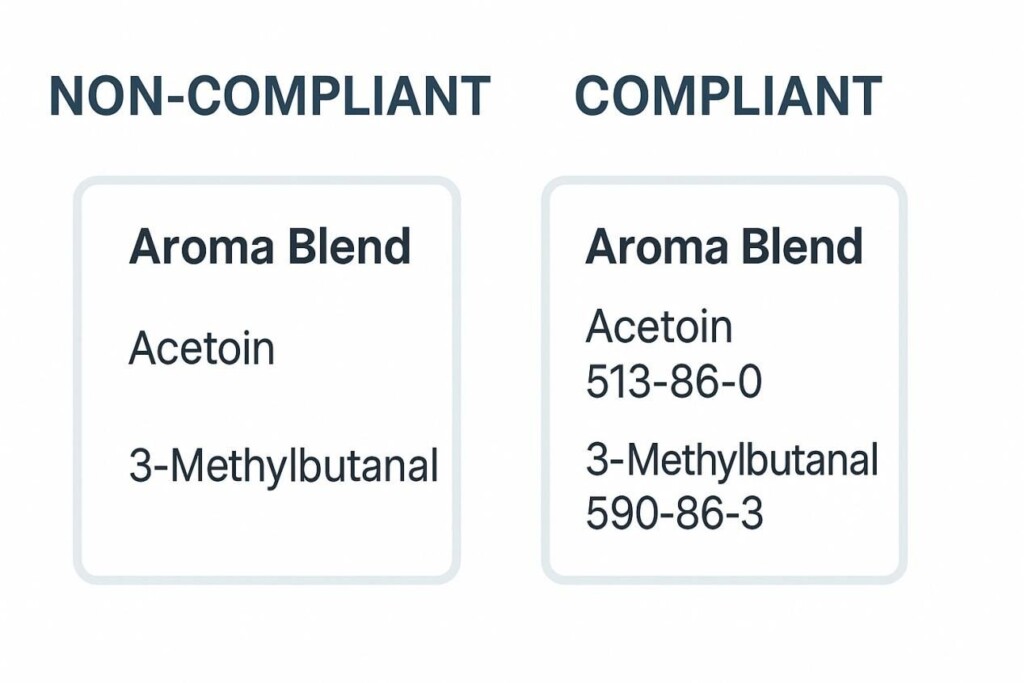
Aroma Blend Label Compliance Comparison
Proper labeling does more than satisfy law—it strengthens competitive positioning:
China Daily emphasized in a 2024 industry report:
“Compliance readiness is no longer optional—it is a decisive factor shaping long-term competitiveness in China’s maturing vape industry.”
(Source: China Daily, 2024, Industry News Section)
Several trends are shaping the next decade:
Manufacturers that invest early in digital and analytical labeling systems will be future-proof.

Futuristic Vape Compliance Label
Labeling aroma blends in China is far from a clerical task—it is a high-stakes intersection of chemistry, law, and strategy. Aroma suppliers must not only disclose ingredients but also demonstrate scientific rigor, ensure regulatory alignment, and build client trust.
At CUIGUAI Flavoring, we integrate advanced GC–MS analysis, toxicological evaluation, and regulatory expertise to produce aroma blend labels that are both compliant and strategically valuable. Our philosophy is that compliance is not a burden—it is a competitive advantage.
Contact us today for a technical consultation with our expert flavorists or to request a free sample tailored to your application:
Contact our QA & R&D team at:
📩 [info@cuiguai.com]
📞 [+86 189 2926 7983]
Or request samples via our site: [www.cuiguai.com]
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy