The explosion of DIY vape brands and small-batch mixers has redefined the creative potential within the vaping industry. With readily available tools and ingredients, hobbyists and aspiring entrepreneurs now formulate their own e-liquids, often sharing recipes across online communities or selling directly to local markets. However, beneath this wave of innovation lurks a technical risk that many overlook: flavor solubility and phase separation. Unlike visible defects, solubility issues often go unnoticed during early production, only manifesting as product failures during storage or use.
Poor flavor solubility isn’t just an aesthetic flaw—it signals fundamental incompatibility within the formula that can degrade product performance, create regulatory issues, and cause long-term brand damage. This blog explores the technical foundations of e-liquid homogenization, common mistakes made by DIY formulators, and actionable steps for building scientifically sound, stable e-liquid blends.

E-Liquid Bottle Comparison Chart
Flavor solubility refers to the ability of the aromatic compounds and solvents in a flavoring concentrate to dissolve uniformly within the base medium of an e-liquid—typically a mixture of Propylene Glycol (PG), Vegetable Glycerin (VG), and sometimes ethanol or other carriers. When solubility fails, the solution separates into layers or exhibits inconsistencies in taste, vapor performance, and color.
While PG is often described as the better solvent due to its low viscosity and high polarity, many flavor molecules—especially non-polar or semi-polar ones like vanillin, menthone, limonene, or esters—require more than just PG to stay dispersed. For example:
This makes the PG/VG ratio a contributing factor, not a solution. Co-solvents like ethanol or emulsifiers such as polysorbate 80 are often used industrially to achieve full dispersion.
Solubility involves a solid or semi-solid compound dissolving in a liquid; miscibility refers to two liquids forming a homogeneous mixture. Many flavor concentrates are complex emulsions of oils, esters, alcohols, and carrier agents. A temporary mixture (from shaking) may seem miscible, but once the kinetic energy fades, non-miscible elements separate.
DIY mixers often assume that once something looks mixed, it is mixed. However, long-term storage will always reveal incompatibilities.
At a molecular level, polar and non-polar substances do not mix well without assistance. PG and VG are both polar solvents, while many flavor oils (such as citrus terpenes or essential oils) are non-polar. This difference in polarity causes repulsion unless bridged with emulsifiers or via physical dispersion methods like ultrasonic treatment.
Real-world analogy: Mixing oil and water—no matter how much you shake them, they separate.
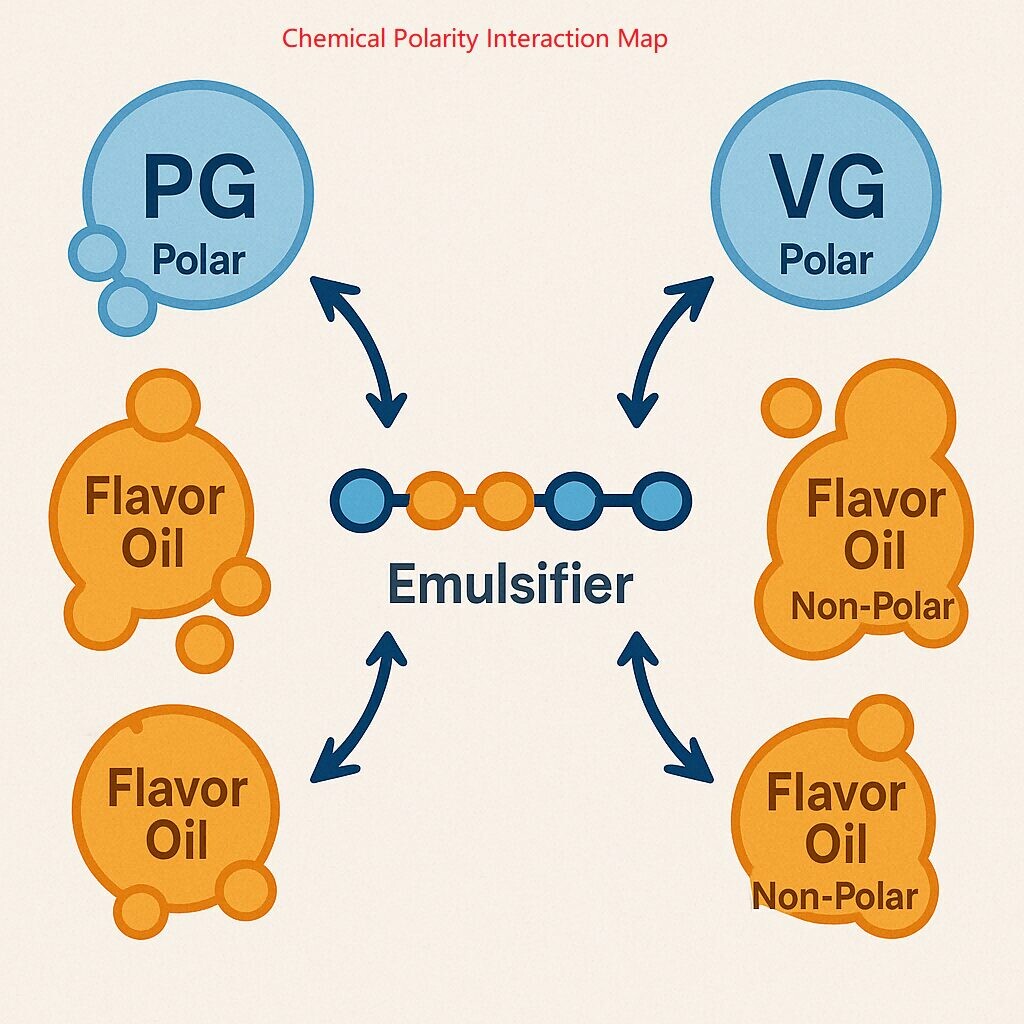
Chemical Polarity Interaction Map
When a vape liquid is not fully homogenized:
In severe cases, users may wrongly attribute poor performance to the device, nicotine, or brand credibility, overlooking the real culprit: poor solubility.
Homogenization is the physical process of uniformly dispersing flavor droplets into the base liquid, typically via shear force, ultrasonic cavitation, or nano-emulsification.
Hand-shaking only introduces temporary kinetic energy. Once the motion ceases, incompatible compounds separate. High-shear mixing, on the other hand, uses rotating impellers or rotor-stator devices to break down flavor droplets into micron- or nanometer-scale particles, improving stability.
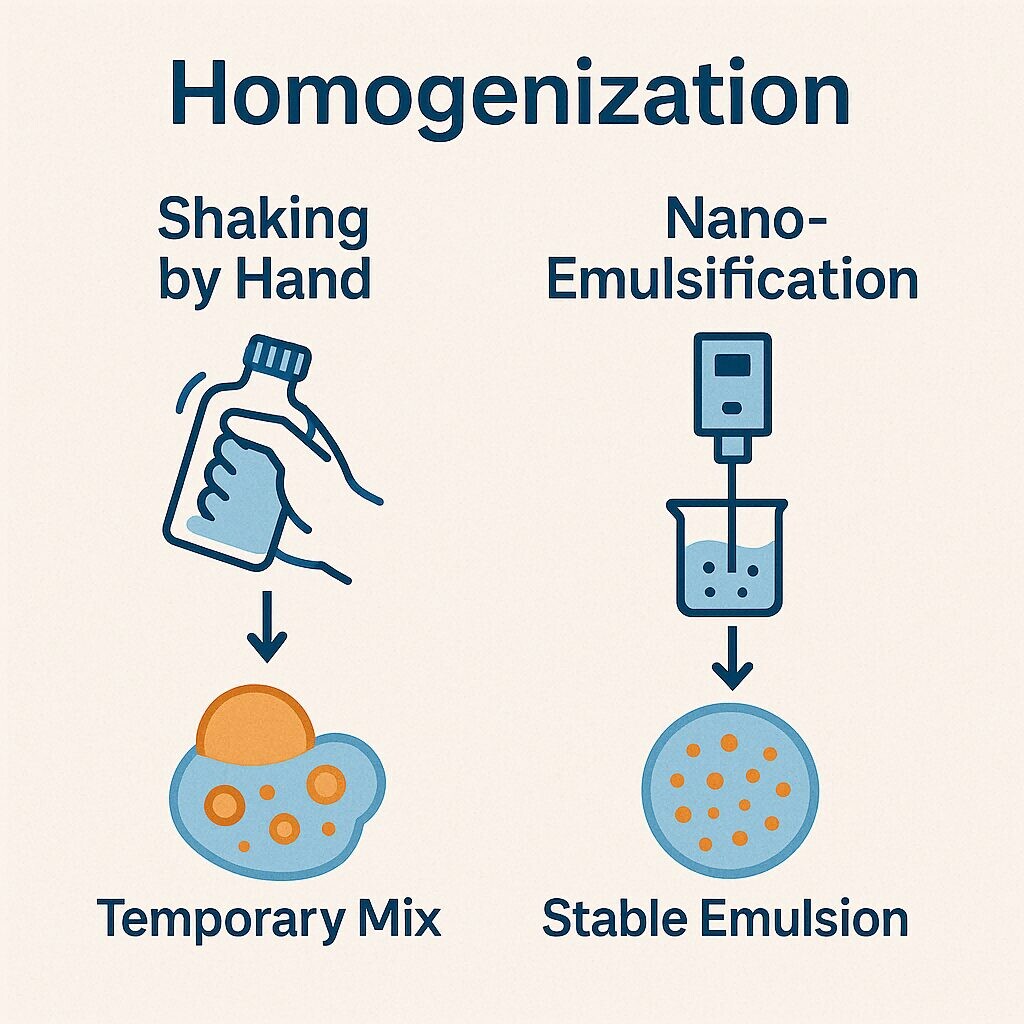
Homogenization Flowchart
Properly homogenized liquids resist flavor drift, discoloration, and viscosity changes during storage. This leads to:
Online forums and YouTube tutorials frequently share tips on warming bottles, vigorous shaking, or adding a dash of vodka as a fix for separation. While well-intended, these methods are insufficient for ensuring long-term product stability.
Startups or hobbyists often avoid investing in lab-grade equipment or proper testing protocols due to cost or lack of technical knowledge. However, skipping this step introduces downstream risks.
White-label operations purchasing bulk concentrates and blending them in-house without solubility testing risk legal exposure. If a customer experiences harsh vapor or device failure due to phase separation, the blame falls on the seller—not the flavor manufacturer.
Regulatory scrutiny is increasing. Brands must be able to demonstrate:
Use flavor houses that design concentrates for vaping—not food or fragrance use. CUIGUAI Flavoring, for example, offers vape-specific flavor solutions built for solubility across PG/VG ratios, with built-in emulsifiers and carrier optimization.
Modern flavor systems often use blended carriers like:
Such carriers help reduce the polarity gap between flavor oils and PG/VG base, ensuring better integration.
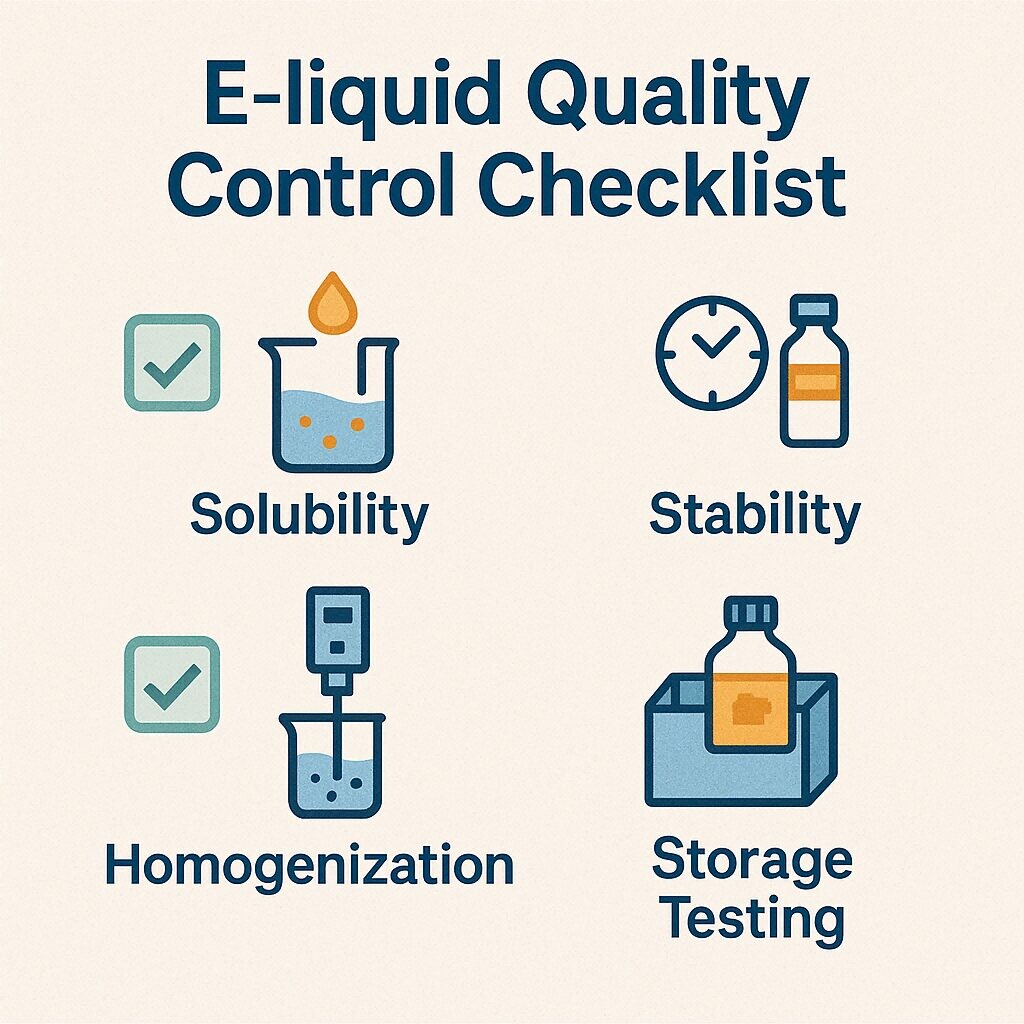
E-liquid Quality Control Checklist
Flavor solubility is not a luxury—it’s a prerequisite for brand viability. DIY brands with scalable ambitions must learn to think beyond recipes and focus on formulation science. Inconsistent batches, phase separation, or device performance issues all stem from overlooked chemistry.
If you plan to build a sustainable vape business, prioritize solubility from the start. This means sourcing solubility-tested concentrates, using the right equipment, and following scientifically valid protocols. It’s the only path to earning long-term trust from customers and regulators alike.
Recommended Partner: CUIGUAI Flavoring – Specializing in high-solubility, pre-homogenized vape flavor solutions that eliminate the risks of DIY separation. Their R&D-backed offerings support consistent performance, even under challenging PG/VG blends.
Keywords: vape solubility issue, DIY flavor separation, e-liquid homogenization, CUIGUAI Flavoring, vape formulation stability, PG/VG compatibility, flavor oil separation, nano-emulsion vape, DIY vape formulation, e-liquid phase stability
Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Jun 19, 2025
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy