Comparison chart of breathing methods.
Most vapers—and even many product developers—are acutely aware of flavor intensity, mouthfeel, sweetness, or cooling sensations. But there’s a less visible, often misunderstood contributor to vape satisfaction: retro-nasal olfaction. Commonly referred to as the “aftertaste” or aroma that rises to the nasal cavity from the back of the throat during exhalation, this sensory path is responsible for up to 80% of what we perceive as flavor.
This blog post takes a deep dive into the mechanisms, significance, and design implications of retro-nasal flavor in e-liquid formulation. For R&D professionals, marketing teams, and vape brands striving to elevate sensory experience, understanding this missing dimension is essential. Retro-nasal olfaction is the bridge between technical formulation and user emotional connection.
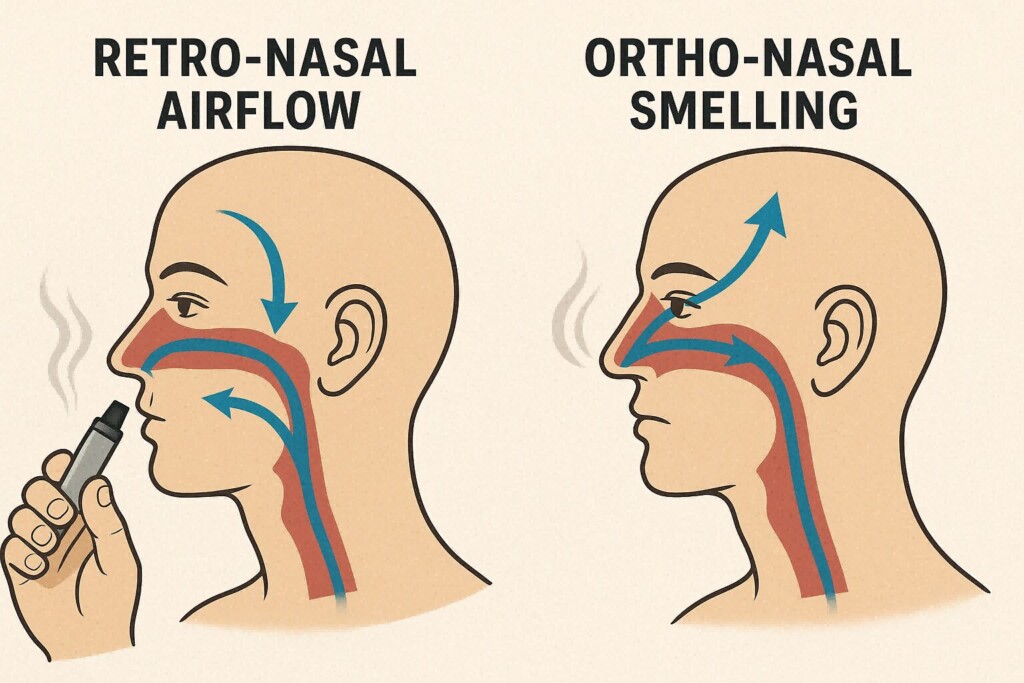
Retro-nasal olfaction is the process by which volatile compounds travel from the oral cavity to the olfactory epithelium via the nasopharynx. It is physiologically distinct from ortho-nasal smelling (via the nostrils) but activates the same sensory receptors in the brain.
While ortho-nasal olfaction refers to the detection of airborne odorants entering through the nose, retro-nasal olfaction pertains to aroma molecules released during exhalation, traveling from the back of the mouth through the nasopharyngeal cavity to the olfactory bulb. Retro-nasal aroma perception is especially critical in activities like eating and vaping, where flavor is not inhaled from the outside environment but emerges from within the oral cavity.
Neuroscientific research confirms that humans rely heavily on retro-nasal cues for distinguishing complex flavors. For example, in blindfolded taste tests with blocked nostrils, most participants struggle to differentiate between apple and pear—even though both have similar sweetness and acidity. This emphasizes the critical role of retro-nasal input.

Anatomy of the olfactory pathway
The human tongue detects only five basic tastes—sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami. Everything else—fruitiness, toastiness, floral notes—comes from olfaction. A vape flavor with high tongue appeal but poor retro-nasal projection will feel one-dimensional.
Retro-nasal aroma adds complexity, character, and realism. For example, a mango flavor might taste flat on the tongue but can evoke the full sensation of ripe tropical fruit if paired with volatile esters that are efficiently delivered retro-nasally.
Flavor longevity in vaping depends not just on vapor density but on the persistence of aromatic compounds. Retro-nasal notes often linger longer than mouth-bound tastes, contributing to what users describe as “satisfying aftertaste” or a “clean finish.” Users tend to associate these lingering effects with quality.
Scents processed retro-nasally are stored in the same olfactory memory pathways as traditional smells. This enhances brand recognition, user loyalty, and emotional response. Signature blends with powerful retro-nasal triggers often become part of a user’s sensory identity—recalling a favorite device, a specific moment, or even a lifestyle image.
Sensory heat map
Effective retro-nasal compounds are typically low-to-medium molecular weight and highly volatile. However, this also makes them vulnerable to thermal degradation. For example, compounds like ethyl butyrate and benzyl acetate deliver vivid fruity notes retro-nasally, but they can decompose if exposed to excessive coil heat.
The solvent system (usually a mix of PG/VG) must be optimized to carry volatile compounds effectively:
Flavor chemists often use co-solvents or emulsifiers to maintain aromatic molecule integrity during vaporization.
Retro-nasal flavor output is highly device-dependent:
Professional flavorists structure e-liquids in layers:
Many terpenes and esters exhibit strong retro-nasal characteristics:
Due to their volatility, these require formulation safeguards like encapsulation or cooling delivery systems to retain effectiveness post-aerosolization.
Carbon-heavy formulas or poor coil hygiene can introduce burnt notes that obliterate subtle aroma signals. Using heat-stable flavoring agents and residue-free carriers enables a cleaner flavor experience.
Timeline of flavor during smoking
R&D teams should construct panels trained in distinguishing ortho-nasal from retro-nasal perception. Techniques include:
Panels should rate both aroma persistence and aromatic evolution throughout the vape cycle.
Advanced equipment helps quantify and validate retro-nasal performance:
Beyond lab tests, user testing remains crucial:
Retro-nasal signals are deeply linked with limbic brain regions governing emotion. This makes them potent triggers for nostalgia, comfort, and pleasure. Smart branding leverages this by associating flavors with lifestyle themes (e.g., “Sunset Peach,” “Forest Calm”).
Most vape brands focus on sweetness and cloud size. Focusing instead on aroma retention and retro-nasal finish is a powerful way to stand out—especially in mature markets where users seek experience, not just intensity.
Educated vapers are more likely to value subtle design. Use packaging, inserts, or social media to teach users about the sensory timeline—helping them appreciate complexity and driving loyalty.
CUIGUAI Flavoring is a leader in formulating e-liquid flavors that don’t just taste good—they finish strong. By engineering blends that optimize both tongue-taste and post-exhale aroma, CUIGUAI supports premium vape experiences across fruit, dessert, herbal, and tobacco categories.
Their approach includes:
CUIGUAI’s laboratory design system ensures that what’s remembered is not just a good puff—but an immersive, lasting aroma journey.
Retro-nasal aroma is not a minor feature—it’s a major dimension of user experience. It links taste to emotion, design to memory, and product to brand identity. Brands that understand and apply retro-nasal science are not only making better flavors—they’re creating deeper connections.
Invest in aroma literacy. Explore the data. Talk to your sensory teams. And choose partners like CUIGUAI Flavoring who understand the science behind satisfaction.

Funnel chart of the impact of flavor perception and user satisfaction.
Keywords: retro-nasal vape aroma, aftertaste vape, olfactory in e-liquids, flavor layering, vape aroma retention, clean burn e-liquid, vapor exhale design.
Description: Discover how retro-nasal olfaction affects flavor perception in vaping and learn how to design e-liquids that deliver memorable, satisfying aftertaste.
Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Jul 01, 2025
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy