In the vaping industry, flavor is more than just an experience — it’s a science. Consumers demand intense, clean, and consistent flavor profiles, but few appreciate the complexity behind maintaining those qualities over time. Flavor degradation is one of the primary reasons for product complaints, returns, and even brand switching. Yet, the traditional solution — adding synthetic preservatives — is increasingly incompatible with modern regulatory frameworks and consumer expectations.
This article explores how e-liquid manufacturers can engineer shelf life at the formulation level. We’ll break down why flavors degrade, the science of flavor stabilization, and practical strategies — including natural antioxidant systems, intelligent carrier design, and microencapsulation — that allow you to preserve flavor freshness without over-preserving.
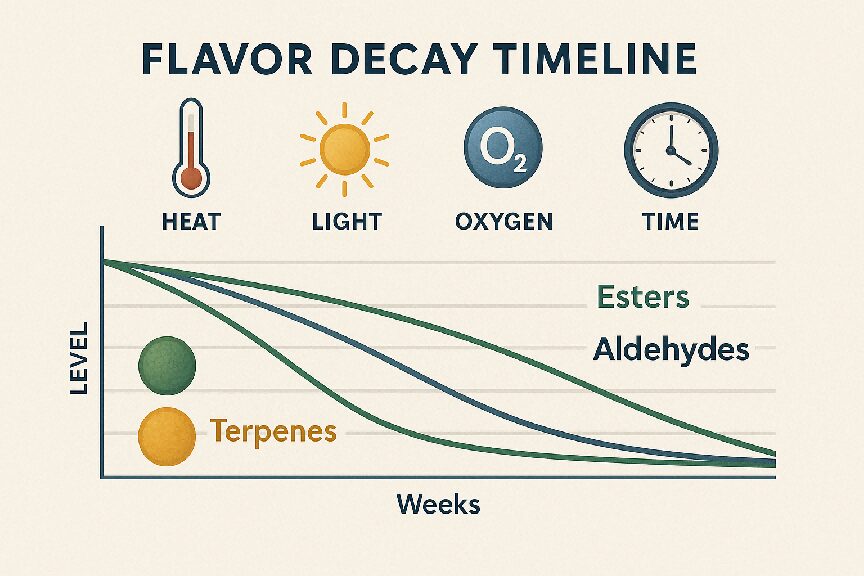
Flavor Decay Timeline
Flavor degradation results from the breakdown of volatile aromatic compounds. This breakdown is accelerated by environmental stressors and chemical instability. Here are the most significant contributors:
One of the most common degradation pathways. Aldehydes, esters, and terpenes react with oxygen, forming off-notes and unpleasant byproducts. Oxidation can occur even in sealed containers due to residual oxygen.
Many vape products are stored or transported at elevated temperatures. High temperatures and UV light accelerate molecular rearrangements, especially in delicate top notes like citrus or floral aromas.
Top notes tend to be highly volatile. Over time, they can evaporate through semi-permeable packaging or react internally, reducing the intensity and complexity of the aroma.
Flavors are sensitive to pH changes, especially in systems with nicotine salts or buffering agents. This can trigger hydrolysis or ester cleavage, degrading fruity and sweet profiles.
Although e-liquids are inhospitable to most microbes, high humidity can promote hydrolytic degradation or packaging interactions.
Shelf life is a delicate balance of chemistry and vapor performance. An e-liquid must remain chemically stable yet still perform aromatically upon vaporization. This depends on several factors:
To optimize shelf life, formulations must consider:
Synthetic preservatives can solve stability issues but create unintended consequences:
| Preservative | Purpose | Drawback |
| BHA/BHT | Antioxidants | Regulatory limits, flavor off-notes |
| Benzoic Acid | Microbial suppression | Harshness, allergic sensitivity |
| EDTA | Metal chelation | Non-natural, label avoidance |
Overuse of preservatives can result in:
Consumers increasingly look for “clean-label” e-liquids — meaning no artificial preservatives, colors, or synthetic emulsifiers. Brands must strike a balance between protecting flavor and maintaining trust.
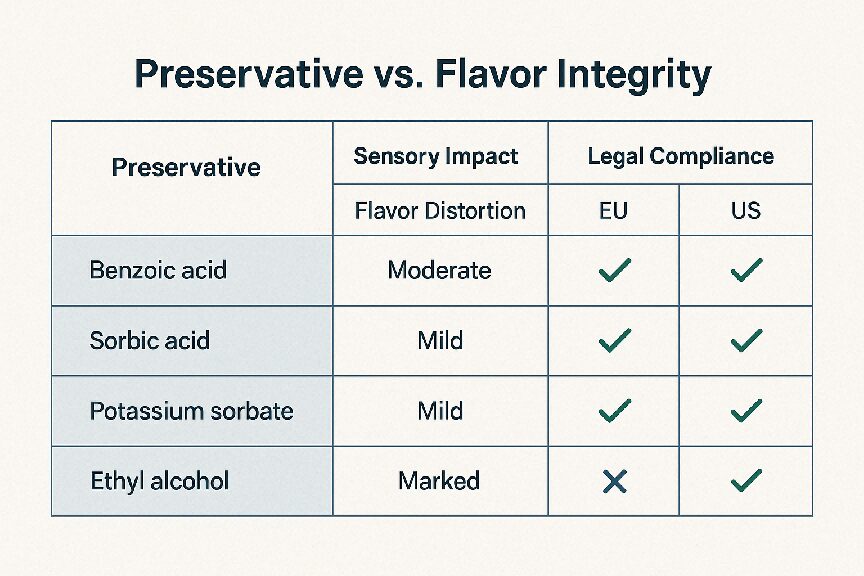
Preservative vs. Flavor Integrity
To extend shelf life without synthetics, formulators can adopt several science-backed techniques:
Natural antioxidants like rosemary extract, grape seed oil, or vitamin E (tocopherols) help reduce oxidative degradation.
Using longer-chain esters and cyclic terpene alcohols improves stability:
Citric acid and gluconic acid buffer the system. Natural chelators like phytic acid help bind trace metals that catalyze flavor breakdown.
Though vape formulas are mostly water-free, trace water activity can influence flavor hydrolysis. Using hygroscopic carriers (like propylene glycol) mitigates this risk.
Microencapsulation is a technology that protects flavor compounds by enclosing them in microscopic capsules. These capsules:
Common materials: maltodextrin, alginate, modified starches
Benefits:
Carrier systems also matter:
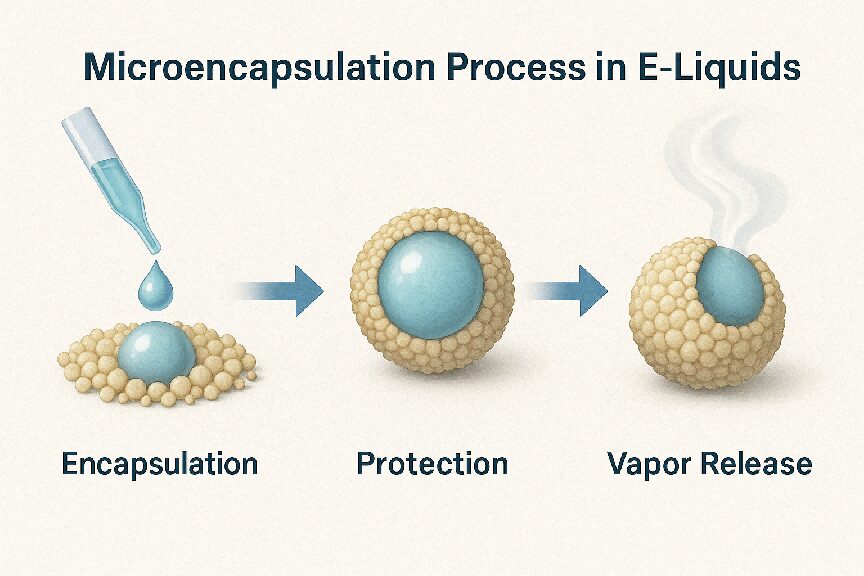
Microencapsulation Process in E-Liquids
CUIGUAI Flavoring has developed a science-forward approach to flavor stabilization, focusing on:
They screen all formulas under accelerated shelf-life testing:
CUIGUAI’s Lemon Ice series maintained 93% top-note integrity after 12 months under real-world storage. Their berry mint profile retained color, aroma, and taste with no synthetic preservatives.
Challenge: Citrus flavors like lemon, orange, and lime are volatile and degrade easily, losing their brightness in as little as 3 months.
Solution:
Result: Over 12 months, sensory integrity loss was under 7%, with no off-notes detected. Consumer panels rated the aged product as “fresh-tasting” even after 300 days.
Longer-lasting flavors aren’t just about taste — they’re about compliance:
CUIGUAI uses accelerated stability protocols aligned with ICH guidelines, helping brands:
Preservation shouldn’t start in the warehouse — it must begin in the lab. By choosing smart ingredients, optimizing carrier systems, and using advanced technologies like microencapsulation, brands can achieve clean-label longevity.
Flavor is fragile, but science makes it resilient. Build your formula for time.
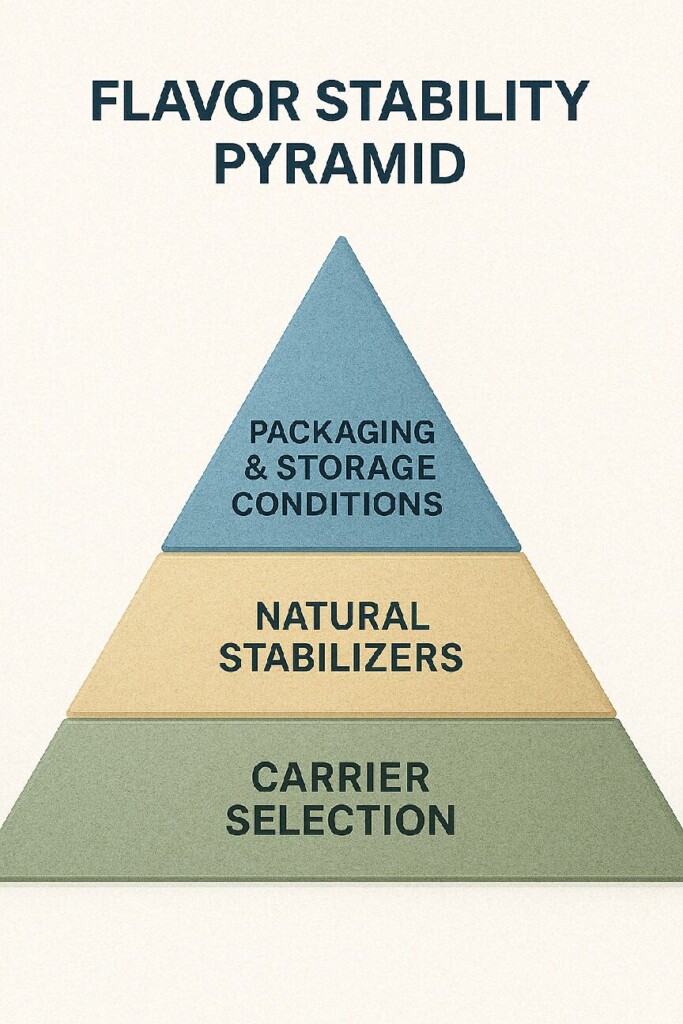
Flavor Stability Pyramid
Keywords: flavor preservation, vape formula shelf life, non-artificial stabilizers
Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Jun 14, 2025
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy